Ovarian Cyst Treatment
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that grow inside or on top of one (or both) ovaries. A cyst is a general term used to describe a fluid-filled structure. Ovarian cysts are usually asymptomatic, but pain in the abdomen or pelvis is common.
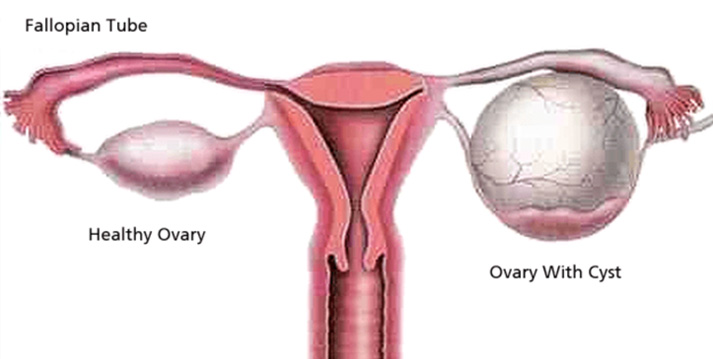
The ovaries are reproductive organs in women that are located in the pelvis. One ovary is on each side of the uterus, and each is about the side of a walnut. The ovaries produce eggs and the female hormones, estrogen and progesterone. The ovaries are the main source of female hormones that control sexual development including breasts, body shape, and body hair. The ovaries also regulate the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Diagnosis
A cyst on your ovary can be found during a pelvic exam. Depending on its size and whether it's fluid filled, solid or mixed, your doctor likely will recommend tests to determine its type and whether you need treatment. Possible tests include:
Pregnancy test. A positive test might suggest that you have a corpus luteum cyst.
Pelvic ultrasound. A wandlike device (transducer) sends and receives high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to create an image of your uterus and ovaries on a video screen. Your doctor analyzes the image to confirm the presence of a cyst, help identify its location and determine whether it's solid, filled with fluid or mixed.
Laparoscopy. Using a laparoscope — a slim, lighted instrument inserted into your abdomen through a small incision — your doctor can see your ovaries and remove the ovarian cyst. This is a surgical procedure that requires anesthesia.
CA 125 blood test. Blood levels of a protein called cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) often are elevated in women with ovarian cancer. If your cyst is partially solid and you're at high risk of ovarian cancer, your doctor might order this test.
Elevated CA 125 levels can also occur in noncancerous conditions, such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Treatment
Treatment depends on your age, the type and size of your cyst, and your symptoms. Your doctor might suggest:
Watchful waiting. In many cases you can wait and be re-examined to see if the cyst goes away within a few months. This is typically an option — regardless of your age — if you have no symptoms and an ultrasound shows you have a simple, small, fluid-filled cyst.
Medication. Your doctor might recommend hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, to keep ovarian cysts from recurring. However, birth control pills won't shrink an existing cyst.
Surgery. Your doctor might suggest removing a cyst that is large, doesn't look like a functional cyst, is growing, continues through two or three menstrual cycles, or causes pain.